


One primary area of cloud research with the CAR instrument is the diffusion domain studies of optically thick and horizontally extended (e.g. marine stratocumulus) cloud decks. From a position deep within an optically thick and horizontally extensive cloud layer, it is possible to derive quantitative information about cloud absorption properties from angular distribution of scattered radiation
Within this region, known as the diffusion domain, the diffuse radiation field assumes an asymptotic form characterized by two rather simple properties.
→ The angular intensity field at the shortest wavelength follows very nearly the cosine function expected for conservative scattering in the diffusion domain.
→ The angular intensity field becomes increasingly anistropic as absorption increases. This is especially noticeable at 2.00 µm where water has the greatest absorption.
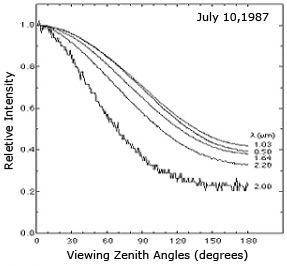
CAR relative intensity as a function of scan angle in the diffusion domain.